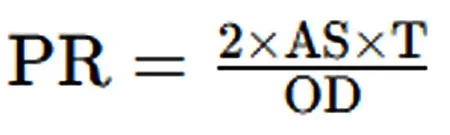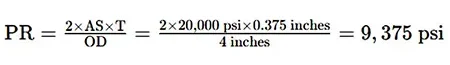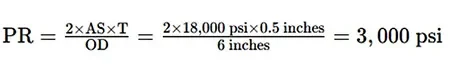Table of Contents
Introduction
Calculating the stainless steel pipe pressure rating is essential for selecting the right materials and ensuring system safety. This guide provides a straightforward approach to help you determine the correct pressure rating for your application.
Methods for Calculating the Stainless Steel Pipe Pressure Rating
Definition and Significance of Pressure Rating
- Concept and Role of Pressure Rating of Pipes: The stainless steel pipe pressure rating is the maximum pressure it can withstand without failure. It plays a critical role in designing safe and efficient fluid transportation systems.
- Classification and Standards of Pressure Rating: Pressure ratings are classified based on material properties and design. Standards such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) provide guidelines for pressure ratings.

Formulas and Steps for Pressure Rating Calculation
Derivation of Pressure Rating Calculation Formulas:

formula of pressure rating for stainless steel pipe
Detailed Explanation of Stainless Steel Pipe Pressure Rating Calculation Steps:
1. Gather Required Information
- Allowable Stress (AS): Obtain from material specifications.
- Wall Thickness (T): Measure the pipe’s wall thickness.
- Outside Diameter (OD): Measure the pipe’s outside diameter.
2. Calculate Pressure Rating (PR)
Substitute Values
- Unit Consistency: Ensure consistent units (e.g., inches for dimensions, psi for stress).
Considerations for Stainless Steel Pipe Pressure Rating Calculator
Influence of Material Properties and Thickness:
- Material Properties: Different stainless steel grades have varied allowable stresses. Choose the grade based on application requirements.
- Wall Thickness: Thicker walls increase pressure rating. Consider corrosion allowances if necessary.
Factors to Consider for Temperature and Medium:
- Temperature: High temperatures reduce allowable stress. Refer to temperature correction factors.
- Medium: Corrosive or abrasive mediums may require higher pressure ratings. Choose grades with appropriate corrosion resistance.
Practical Application Cases
Chemical Plant Pipeline System
In a chemical plant, a pipeline system is required to transport corrosive chemicals at varying pressures. The system must maintain integrity, prevent leaks, and resist corrosion to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Scenario
A chemical plant needs to transport sulfuric acid, a highly corrosive chemical, through a pipeline system.
Requirements
- Operating Pressure: 150 psi
- Corrosion Resistance: High resistance to sulfuric acid
Selection Criteria
- Material Choice: Select Grade 316L stainless steel for its excellent corrosion resistance to sulfuric acid.
- Wall Thickness: Calculate the required wall thickness using the stainless steel pipe pressure rating formula to ensure a safety factor.
- Pipe Size: Choose a suitable pipe size to accommodate the required flow rate and pressure.
Pipe Selection
- Material: Grade 316L stainless steel
- Wall Thickness Calculation:
- Allowable Stress (AS): Consult material specifications (e.g., 20,000 psi)
- Wall Thickness (T): Assume 0.375 inches
- Outside Diameter (OD): 4 inches
- Pressure Rating (PR):
- Safety Margin: Choose a pipe with a higher pressure rating, such as 10,000 psi, to account for safety factors.
Installation and Testing
The Grade 316L stainless steel pipes are installed according to ASME B31.3 standards for process piping.
Prior to operation, the system undergoes pressure testing to ensure integrity and leak-free performance.
Result
The chemical plant successfully installs Grade 316L stainless steel pipes with a pressure rating of 10,000 psi.
The pipeline system reliably transports sulfuric acid at 150 psi without corrosion or leaks, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Oil Refinery High-Pressure System
An oil refinery requires a high-pressure pipeline system to transport crude oil and refined products. The system must handle high pressures and temperatures, as well as resist corrosion from petroleum products.
Scenario
An oil refinery needs a pipeline system to transport crude oil from storage tanks to processing units at high pressures.
Requirements
- Operating Pressure: 1000 psi
- Temperature: 150°F
- Corrosion Resistance: Resistance to petroleum products
Selection Criteria
- Material Choice: Select Grade 304H stainless steel for its high-temperature strength and resistance to petroleum products.
- Wall Thickness: Calculate the required wall thickness for the given pressure and temperature.
- Safety Margin: Choose a pipe with a higher pressure rating to ensure safety under varying conditions.
Pipe Selection
- Material: Grade 304H stainless steel
- Wall Thickness Calculation:
- Allowable Stress (AS): Refer to material specifications (e.g., 18,000 psi)
- Wall Thickness (T): Assume 0.5 inches
- Outside Diameter (OD): 6 inches
- Pressure Rating (PR):
- Safety Margin: Choose a pipe with a pressure rating of 3500 psi for added safety.
Installation and Testing
The Grade 304H stainless steel pipes are installed according to ASME B31.3 standards for high-pressure piping.
Pressure tests are conducted to ensure the system can safely operate at 1000 psi and 150°F.
Result
The oil refinery successfully installs Grade 304H stainless steel pipes with a pressure rating of 3500 psi.
The pipeline system reliably transports crude oil at 1000 psi and 150°F, meeting the refinery’s requirements for high-pressure operation.
Water Treatment Plant Hygienic System
A water treatment plant requires a hygienic pipeline system to transport clean water for municipal supply. The system must be sanitary, easy to clean, and resistant to bacterial growth.
Scenario
A water treatment plant needs a pipeline system to transport treated clean water to municipal supply lines.
Requirements
- Hygiene Standard: ASTM A270 for food and beverage industries
- Sanitation: Smooth, crevice-free surfaces to prevent bacterial growth
Selection Criteria
- Material Choice: Select ASTM A270 stainless steel pipes for their hygienic design and easy cleanability.
- Pipe Size: Choose suitable pipe sizes to meet the required flow rates for clean water supply.
Pipe Selection
- Material: ASTM A270 stainless steel
- Size: 2-inch diameter pipes
- Sanitation: Crevice-free design for easy cleaning and prevention of bacterial growth
Installation and Testing
The ASTM A270 stainless steel pipes are installed according to hygienic standards.
Prior to operation, the system undergoes inspection to ensure cleanliness and hygienic integrity.
Result
The water treatment plant successfully installs ASTM A270 stainless steel pipes with a 2-inch diameter.
The pipeline system transports treated clean water with hygienic integrity, meeting sanitation standards and municipal supply requirements.
How to Choose the Right Pipes According to Pressure
When selecting stainless steel pipes for a system, it’s essential to consider the operating pressure to ensure safety and efficiency. Here are steps to guide the selection process:
Identify Operating Pressure
Determine the maximum pressure the system will experience during normal operation.
This is typically specified by engineering requirements or can be calculated based on system parameters.
Refer to SS Pipe Pressure Rating Tables
Manufacturers often provide stainless steel pipe pressure rating tables for different pipe sizes and stainless steel grades.
These tables list the maximum allowable pressure for each pipe size and grade combination.
Match the operating pressure of the system with the corresponding stainless pipe pressure rating from the tables.
Apply Safety Margins
It is prudent to choose a pipe with a pressure rating higher than the system’s operating pressure.
This additional margin of safety helps account for potential pressure spikes, system variations, or unforeseen circumstances.
A common practice is to select a pipe with a pressure rating at least 25% higher than the maximum operating pressure.
Consider Environmental Factors
The environment in which the system operates can affect the choice of stainless steel grade.
Corrosive environments, such as those with exposure to chemicals or saltwater, may require higher corrosion-resistant stainless steel grades.
Consider the temperature and medium being transported as these factors can impact the material’s performance.
Calculate Required Wall Thickness
The wall thickness of the pipe is crucial in determining its pressure rating.
Use the stainless steel pipe pressure rating formula to calculate the necessary wall thickness.
Rearrange the formula to solve for wall thickness.
Final Steps
Once the appropriate stainless steel grade, pipe size, and wall thickness are determined:
- Verify compliance with relevant standards such as ASME and ASTM.
- Ensure proper installation according to industry guidelines.
- Conduct pressure testing to confirm system integrity.
Related Standards
International Standards
ASTM Standards
- ASTM A312 – Seamless and Welded Stainless Steel Pipes
- ASTM A269 – Seamless and Welded Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubing
- ASTM A358 – Electric-Fusion-Welded Austenitic Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Pipe
EN Standards
- EN 10216 – Seamless steel tubes for pressure purposes
- EN 10217 – Welded steel tubes for pressure purposes
- EN 10296 – Welded circular steel tubes for mechanical and general engineering purposes
Domestic Standards – China
GB Standards
- GB/T 14975 – Seamless Stainless Steel Tubes for Structure
- GB/T 14976 – Seamless Stainless Steel Pipes for Fluid Transport
- GB/T 12771 – Welded Stainless Steel Pipes for Liquid Delivery
SY Standards (Sinopec Standards)
- SY/T 6905 – Technical Specification for Seamless Stainless Steel Tubing for Oil and Gas Production
- SY/T 5274 – Welded Stainless Steel Pipes for Corrosion-Resistant Oil and Gas Transmission
These standards provide specifications and guidelines for the design, materials, dimensions, testing, and applications of the corresponding stainless steel pipes.
Stainless Steel Tubing Pressure Rating Chart
Here’s a stainless steel pipe pressure rating chart, which typically follows the ASME B31.3 Pressure Piping Code. The pressure ratings depend on the pipe size, schedule (thickness), and material grade. Below is a simplified version for common grades and sizes:
| Pipe Size (inches) | Schedule | Pressure Rating (psi) | Temperature (°F) | Material Grade |
| 1/2 | 40 | 2235 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 1/2 | 80 | 3300 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 1 | 40 | 1885 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 1 | 80 | 3130 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 2 | 40 | 1780 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 2 | 80 | 2850 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 4 | 40 | 1620 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 4 | 80 | 2700 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 6 | 40 | 1450 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 6 | 80 | 2500 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 8 | 40 | 1400 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
| 8 | 80 | 2300 | 100 | 304/304L, 316/316L |
Notes:
- Schedule: Indicates the wall thickness of the pipe. Higher schedules (e.g., 80) indicate thicker walls and higher ss pipe pressure ratings.
- Pressure Rating: The maximum allowable pressure for the pipe at the given temperature.
- Temperature: The temperature at which the pressure rating applies.
- Material Grade: Common stainless steel grades used in pipes are 304/304L and 316/316L.
For more detailed information and specific conditions, it’s important to refer to the ASME B31.3 code and manufacturer specifications.
Conclusion
Accurately calculating the stainless steel pipe pressure rating helps maintain safety and optimize performance. Use these steps to make informed choices for your piping system.
If you need more specific data or different conditions, please visit ALLOYXPERT!
Read More: